Common Concepts of TCUP¶
Introduction¶
The following are the important concepts of TCUP which any TCUP user/developer needs to understand.
Multi-tenancy¶
TCUP supports multi-tenancy allowing multiple users’/ tenant’s data to be stored in the same physical data store but logically separated by tenant identifier.
API Key¶
API Key is a unique identifier for a tenant used for user authentication.
Docker¶
Docker is a software platform designed to make it easier to create, deploy and run applications by using containers. It allows developers to package up an application with all the parts it needs in a container and then ship it out as one package.
Geo-fencing¶
Geo-fencing (geofencing) is a feature in a software program that uses the Global Positioning System (GPS) or Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) to define geographical boundaries.
The technology has many practical uses. For example, a network administrator can set up alerts so when a hospital-owned iPad leaves the hospital grounds, the administrator can disable the device. Similarly a marketer can geo-fence a retail store in a mall and send coupons to any customer (who has downloaded a particular mobile app) whenever the customer (and his smart phone) crosses the boundary.
This feature has been incorporated in message routing rules. The rule will define the specific boundaries and when a particular sensor enters or exits the boundary an alert will be triggered.
If one wants to use the geofencing feature they just need to set “geoFencing”: “YES” in the rule JSON while creating the rule.
Elastic Search¶
Elasticsearch is a search server based on Lucene. It provides a distributed, multitenant-capable full-text search engine with a HTTP web interface and schema-free JSON documents. Elasticsearch is developed in Java and is released as open source under the terms of the Apache License.
Some of the important concepts of Elastic Search are as follows:
Shard - A shard is a single Lucene instance. It is a low-level worker unit which is managed automatically by elasticsearch.
Index - An index is like a database in a relational database. It has a mapping which defines multiple types. It is a logical namespace which maps to one or more primary shards and can have zero or more replica shards.
Mapping - A mapping is like a schema definition in a relational database. Each index has a mapping (which defines each type within the index) and also a number of index-wide settings. A mapping can either be defined explicitly or it gets generated automatically when a document is indexed.
Cluster - A cluster consists of one or more nodes which shares the same cluster name. Each cluster has a single master node which is chosen automatically by the cluster and which can be replaced if the current master node fails.
Note
For more infomation please refer to the following link - https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/glossary.html
Jolt¶
Jolt is a JSON to JSON transformation library written in Java which provides a set of transforms that can be ‘chained’ together to form the overall JSON to JSON transformation. Jolt is used to migrate the backend from Solr/MySql to Cassandra/ElasticSearch.
Action Service uses Jolt schema to transform data to Elastic Search format before inserting.
Jolt tackles each of the following concerns:
Identifies the pieces of the input data that the user cares about and places them in the output JSON.
Handles all the JSON text formatting (comma, closing curly brackets etc.)
Verifies the transform for data and format correctness.
Performs arbitrary custom data manipulations like adding fields together or performing date conversions.
Jolt provides the following features:
shift : copy data from the input tree and put it in the output tree
default : apply default values to the tree
remove : remove data from the tree
sort : sort the Map key values alphabetically
Note
For more infomation please refer to the following link - https://github.com/bazaarvoice/jolt
Syslog¶
Syslog is a standard for message logging. It permits separation of the software that generates messages, the system that stores them and the software that reports and analyzes them. Each message is labeled with a facility code (indicating the software type generating the message) and assigned a severity label.
Computer system designers may use syslog for system management and security auditing as well as general information, analysis and debugging messages. A wide variety of devices such as printers, routers and message receivers across many platforms use the syslog standard. This permits the consolidation of logging data from different types of systems in a central repository. Implementations of syslog exist for many operating systems.
Push Notification¶
Push Notification lets the application notify a user of new messages /events even when the user is not actively using the application. When a device receives a push notification on Android devices, the application’s icon and a message appears in the status bar.
Action Service uses Google Push Notification to deliver messages to user mobile. Users first needs to register their device using Google Cloud Messaging app to Google server and Action Service
Note
For more infomation please refer to the following link - https://developers.google.com/cloud-messaging/gcm
REST API¶
REST (Representational State Transfer) is an architectural style and an approach to communications that is often used in the development of web services. The use of REST is often preferred over the more heavyweight SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) style because REST does not leverage as much bandwidth which makes it a better fit for use over the internet.
The key abstraction of information in REST is a ‘resource’. Any information that can be named can be a resource: a document or image, a temporal service, a collection of other resources, a non-virtual object (e.g. a person), and so on. REST uses a ‘resource identifier’ to identify the particular resource involved in an interaction.
TCUP APIs are RESTful APIs and RESTful APIs follows ‘CURD’ operations as below.
Operations |
Rest API |
|---|---|
C for Create |
Use POST for Creation |
U for Update |
Use PUT for Updating |
R for Read/Retrieve |
Use GET for Retrieving |
D for Delete |
Use Delete for Deleting |
RabbitMQ¶
RabbitMQ is a message-queueing software called a message broker that implements the Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP). It acts like a middleman for various services. The basic architecture of a message queue is simple, there are client applications called producers that create messages and deliver them to the broker (the message queue). Other applications called consumers connects to the queue and subscribes to the messages to be processed. A software can be a producer, a consumer or both. Messages placed onto the queue are stored until the consumer retrieves them.
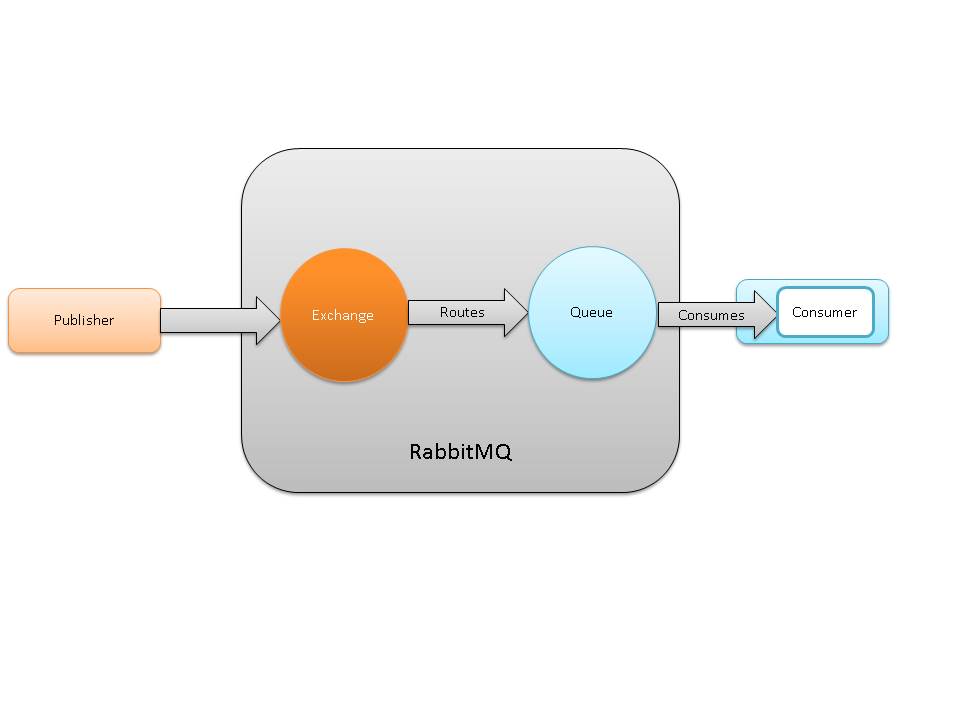
AMQP¶
Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP) is a messaging protocol that enables conforming client applications to communicate with conforming messaging middleware brokers.
Note
For more infomation please refer to the following link - https://www.amqp.org/about/what
DTLS¶
Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) is a communication protocol designed to protect data privacy and prevent eavesdropping and tampering. It is based on the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol that provides security to computer-based communication networks. The main difference between DTLS and TLS is that DTLS uses UDP and TLS uses TCP.
MQTT¶
Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) is an ISO standard publish-subscribe-based messaging protocol. It is designed for connections with remote locations where a ‘small code footprint’ is required or the network bandwidth is limited. An MQTT system consists of clients communicating with a server, often called a ‘broker’. A client may either be a publisher of information or a subscriber. Each client can connect to the broker. This is lightweight messaging protocol which uses a publish/subscribe communication pattern and plays an important role in the internet of things (IoT) by facilitating machine-to-machine (M2M) communication.